Maths Channel
Overview
Maths channels can be used to calculate values from one or more inputs using arithmetic and functions.
The equation entered for a maths channel is referred to as a ‘script’.
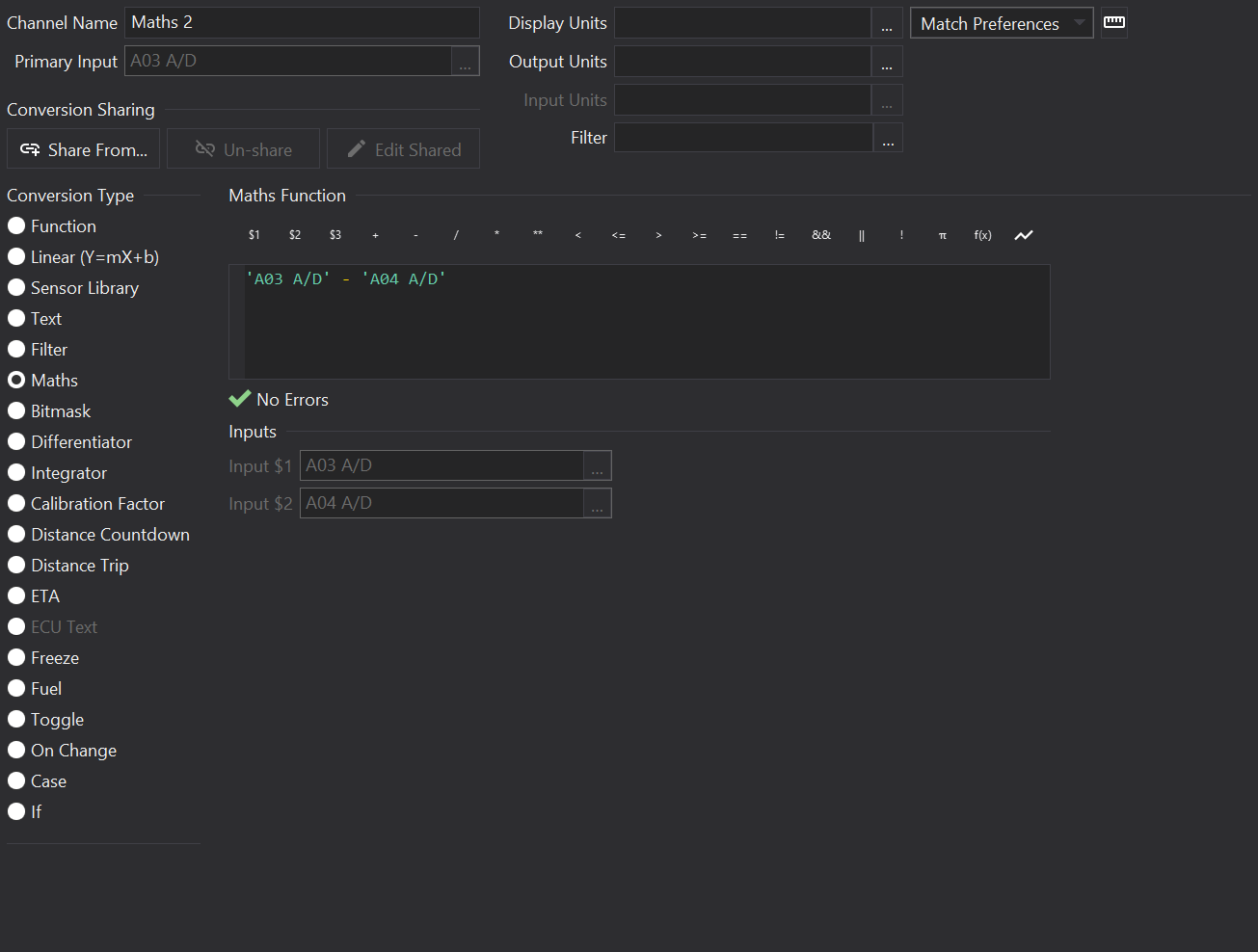

Script Entry
Type in the Maths Function area to enter in your script.
Press Ctrl-Space in the script editor to show function / constant autocomplete.
Below the script entry area, any errors in the script will be shown.
Above the script area are buttons for inserting channels, functions, operators and constants.
Whilst it is generally quicker to type scripts in by hand, the buttons offer a reminder of what’s available.
Input Variables
Input variables may be specified in maths scripts in the form $N where N is a number, e.g. $1 or $5. Up to 64 input variables may be specified.
If input variables are used then the inputs may be selected underneath the script entry area.
For example, to multiply two input variables together, you could write:
$1 * $2Inline Channels
As an alternative to Input variables, channels can be specified directly in maths scripts using the channel name in single quotation marks.
e.g.
'Analog 01'When typing a single quote character in the script editor, a list of channels will be shown for auto-completion.
Comments
Comments can be inserted in scripts and start with a # character. They continue to the end of the line. Scripts may span over multiple lines.
# This is a commentOperators
| Operator | Precedence | Description |
|---|---|---|
| () | 1 | Parenthesis for grouping expressions, e.g. ('x' + 'y') * 4 |
| ** | 2 | Exponentiation (x ** y => xy) |
| * | 3 | Multiplication |
| / | 3 | Division |
| % | 3 | Modulo (remainder of integer division) |
| + | 4 | Addition |
| - | 4 | Subtraction |
As with normal algebra, multiplication of terms takes precedence over addition and will be applied first. If the precedence is not clear, it is recommended to group expressions using parenthesis.
e.g. in the expression:
1 + 2 * 3 # Multiplication takes precedence over addition so 2 is multiplied by 3 before adding 1.Operators at the same level of precedence are evaluated left-to-right.
Constants
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| E | Eulers number e, 2.718281… |
| PI | Pi (π), 3.141592… |
| PHI | Golden Ratio, Phi (φ), 1.618033… |
| true | Boolean 1. |
| false | Boolean 0. |
Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| abs(x) | Returns the absolute value of ‘x’, |
| exp(x) | Returns the natural exponential of ‘x’, ex. |
| log10(x) | Returns the base 10 logarithm of ‘x’. |
| ln(x) | Returns the natural (base e) logarithm of ‘x’. |
| min(x1, x2 …xN) | Returns the minimum value of x1…xN. |
| max(x1, x2 …xN) | Returns the maximum value of x1…xN. |
| pow(x, y) | Returns x raised to the power of y; xy. |
| sgn(x) | Returns the 1 if ‘x’ is positive, -1 if ‘x’ is negative and 0 if ‘x’ is zero. |
| sqr(x) | Returns the square of ‘x’. |
| sqrt(x) | Returns the square root of ‘x’. |
Trigonometric Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| acos(x) | Returns the arc-cosine (inverse cosine) of ‘x’, in radians. |
| asin(x) | Returns the arc-sine (inverse sine) of ‘x’, in radians. |
| atan(x) | Returns the arc-tangent (inverse tangent) of ‘x’, in radians. |
| cos(x) | Returns the cosine of ‘x’ (in radians). |
| sin(x) | Returns the sine of ‘x’ (in radians). |
| tan(x) | Returns the tangent of ‘x’ (in radians). |
Supported By Displays
| Display | Supported? |
|---|---|
| CD34 | Yes |
| LDS4 | Yes |
| CD32 | Yes |
| LDS35 | Yes |
| LDS35_L | Yes |
| CD6-43 | Yes |
| GLW-43 | Yes |