Linear (Scalar) Channel
Overview
This is one of the most commonly used channel types. The channel is scaled using a linear scaling equation y = mx + c - i.e a multiplier and offset.
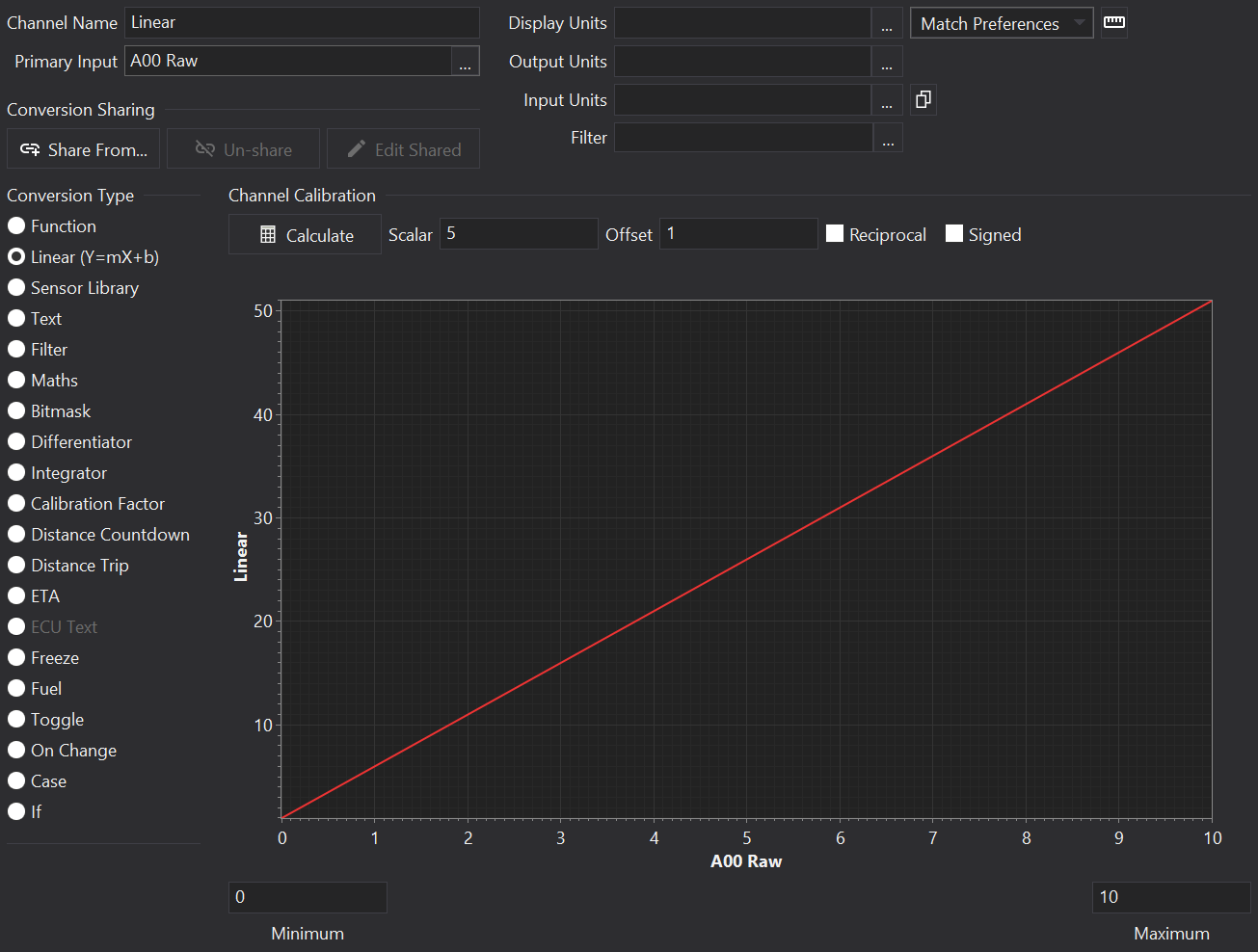

Settings
Scalar
The multiplier value (m in y = mx + c).
Offset
Added to the value after applying the multiplier (c in y = mx + c).
Signed
If ‘signed’ is checked then raw input values are treated as twos-complement numbers.
Reciprocal
If ‘reciprocal’ is checked then the scaling equation takes the form y = (1 / x) * scalar + offset. If the input value is zero then the result will be the special floating point value NaN (Not a Number).
Graph
The graph shows the scaling relationship.
Minimum
Sets the minimum value to show on the X-axis of the graph. This has no effect on the setup when running on the display.
Maximum
Sets the maximum value to show on the X-axis of the graph. This has no effect on the setup when running on the display.
Calculation from Reference Values
If a pair of reference values for input vs output are available (e.g. from a sensor data-sheet), click the Calculate button () and enter in the values. Clicking OK will compute the scalar and offset required to fit the pair of points.
Supported By Displays
| Display | Supported? |
|---|---|
| CD34 | Yes |
| LDS4 | Yes |
| CD32 | Yes |
| LDS35 | Yes |
| LDS35_L | Yes |
| CD6-43 | Yes |
| GLW-43 | Yes |